Newsletter
CASE STUDY: Point Mutation Correction in a Patient-Derived iPSC
Goal: To correct a point mutation (AGC > GGC) in a gene associated with neurological disorders in a patient derived iPSC line and generate a homozygous wildtype line.
1. Patient-derived iPSCs were obtained from the patient and the cell line validated. The sequence at the desired locus (neurological gene) was confirmed to be a heterozygous mutation (AGC/GGC).
Figure 1. Schematic representation of the workflow undertaken for the project.
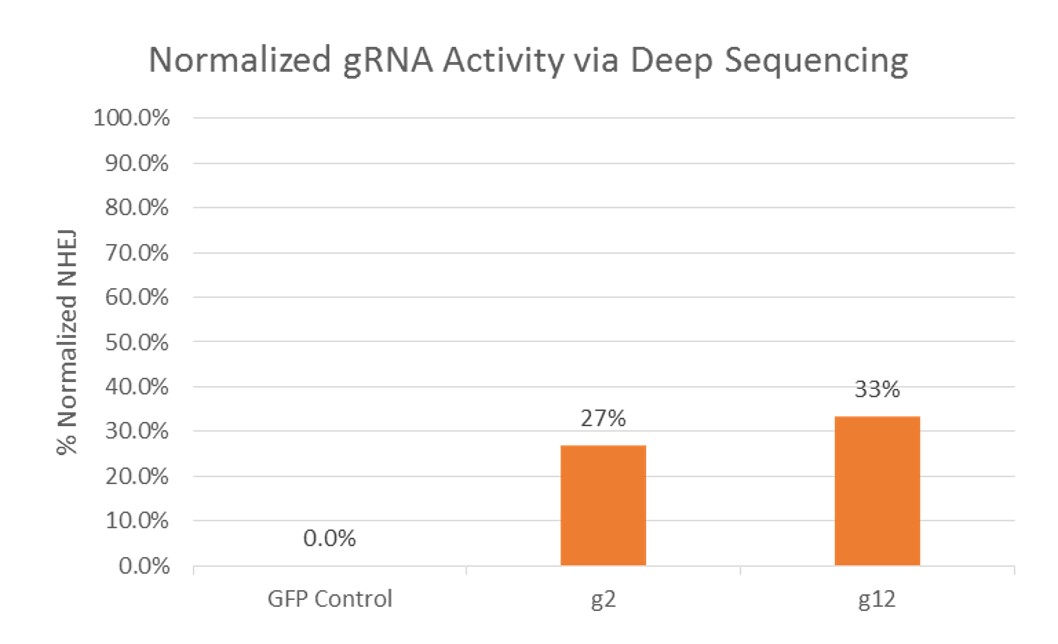
2. After cell line validation and confirming presence of mutation in the desired gene, two gRNAs were designed and validated by mismatch detection assay in K562 cells and frequency of NHEJ events as a result of the gRNA-Cas9 complex and DSB was quantified using next generation/ deep sequencing (NGS).
Figure 2. gRNA Activity via NGS, Normalized by NHEJ frequency resulting from control (GFP) transfection. Results showed that NHEJ frequency mediated by gRNA g1 and g2 were 27% and 33%, respectively. The gRNA g2 was selected for transfection.
3. The Cas/gRNA and donor vectors were transfected into the hiPSCs. After a transient puromycin selection, single cell colonies were isolated and expanded. Individual colonies were then genotyped by PCR and sequencing. Positive clones were expanded, and the genotypes were further confirmed by sequencing.
A. 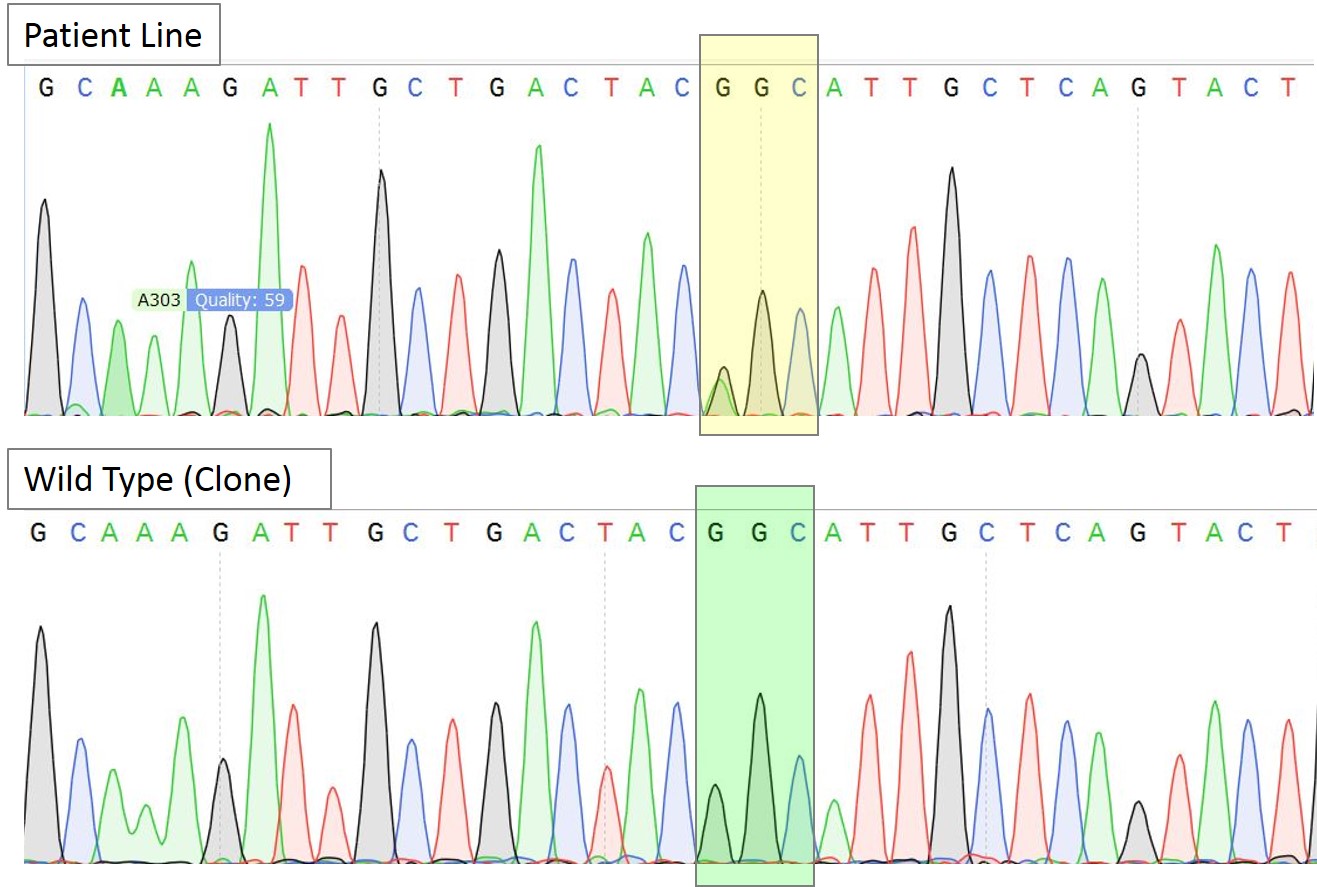
Figure 3A. Sequence chromatogram of the patient line with heterozygous mutation AGC/GGC and a representative homozygous wildtype clone. The yellow box highlights the heterozygous mutation while the green box highlights the correction to homozygous wild type sequence (GGC) in the selected clone.
B. 
Figure 3B. Sequence alignment of representative homozygous clone (WT) and the mutation (the patient line). A silent mutation (GCA; yellow) was introduced in the donor sequence to prevent repeated recognition and cutting by the Cas9/gRNA complex at the modification site. The mutation correction is highlighted in green.