Newsletter
Custom In Vivo Assay Services
As a long-standing leader in genetically engineered animal models, Applied StemCell also offers a comprehensive custom research solutions platform for downstream assays in mouse and rat models. Our state-of-the-art vivarium is equipped with automated cages & devices for behavioral assessments, sample collection and in vivo measurements (ECG, EEG) of the animals. We have a multidisciplinary team of expert scientists who can design a comprehensive project plan to fit any requirement/stage of your research pipeline and for drug discovery and screening.
- Designing and engineering research animal disease models
- Adoptive transfers/transplantation
- In vivo functional screening assays
- End-of-study in vitro assays
Products and Services
Technical Details
We are also NIH Office of Laboratory Animal Welfare (OLAW) Assured and have DEA licenses for Schedule I & II-V drugs. Our project portfolio also comes with dedicated project managers for scheduling, timely communication and completion of your projects.
Below is a selected list of assays available for your in vivo assessments:
1. Disease Model Generation:
- Genetically modified mouse and rat models
- Adoptive cell transfer, teratomas
- Surgically/ drug induced models
2. In Vivo Assays:
- Behavioral assessments: cognition & locomotor activity
- Automated in vivo measurements: ECG, EEG, EMG
- In vivo pharmacokinetics
3. In Vitro / Postmortem Assays:
- Electrophysiology: neuronal & cardiac assays; patch-clamp, MEA
- Tissue collection and end-of-study analyses: western blots, immunohistochemistry, RT-PCR
Don’t see an assay / measurement? Please contact us to discuss your requirements with one of our technical experts.
Applications: Functional genomics, disease modeling, target identification and validation for drug discovery and screening, and many more.
Application Notes
1. Cardiac Ion Channel Safety Screening Using Manual Patch Recording
Screening for potential cardiotoxicity of novel drug candidates that modulate key ion channels. Utilizing our expertise in patch-clamp electrophysiology, drugs can be screened against an array of ion channels including recombinant human ether-a-go-go (hERG), Nav1.5, Cav1.2, and human iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes.
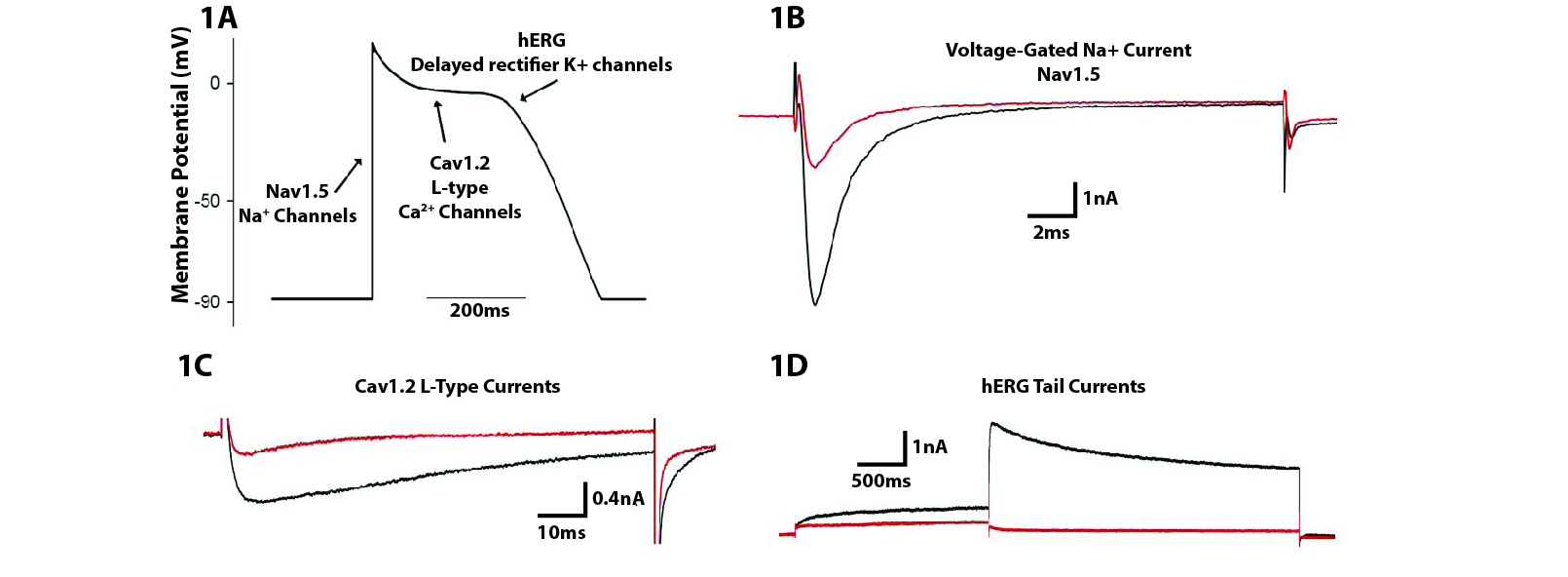
Figure 1. (A) Several ion channels involved in the cardiac action potential are implicated in QT interval prolongation. (B-D) Example recordings showing drug inhibition of human Nav1.5, Cav1.2 and hERG currents. Black traces represent control currents and red traces show currents in the presence of representative inhibitory drugs.
2. Functional Screening Assays to Test Neurological Endpoints Using Patch Clamp Recording
Electrophysiological Recordings in Rodent Brain Slices for disease model validation and drug efficacy/safety. Standard electrophysiological recordings of acutely prepared brain slices are used to measure changes in membrane potential, cell excitability, spike firing and synaptic neurotransmission, including long-term potentiation/ depression (LTP/LTD).
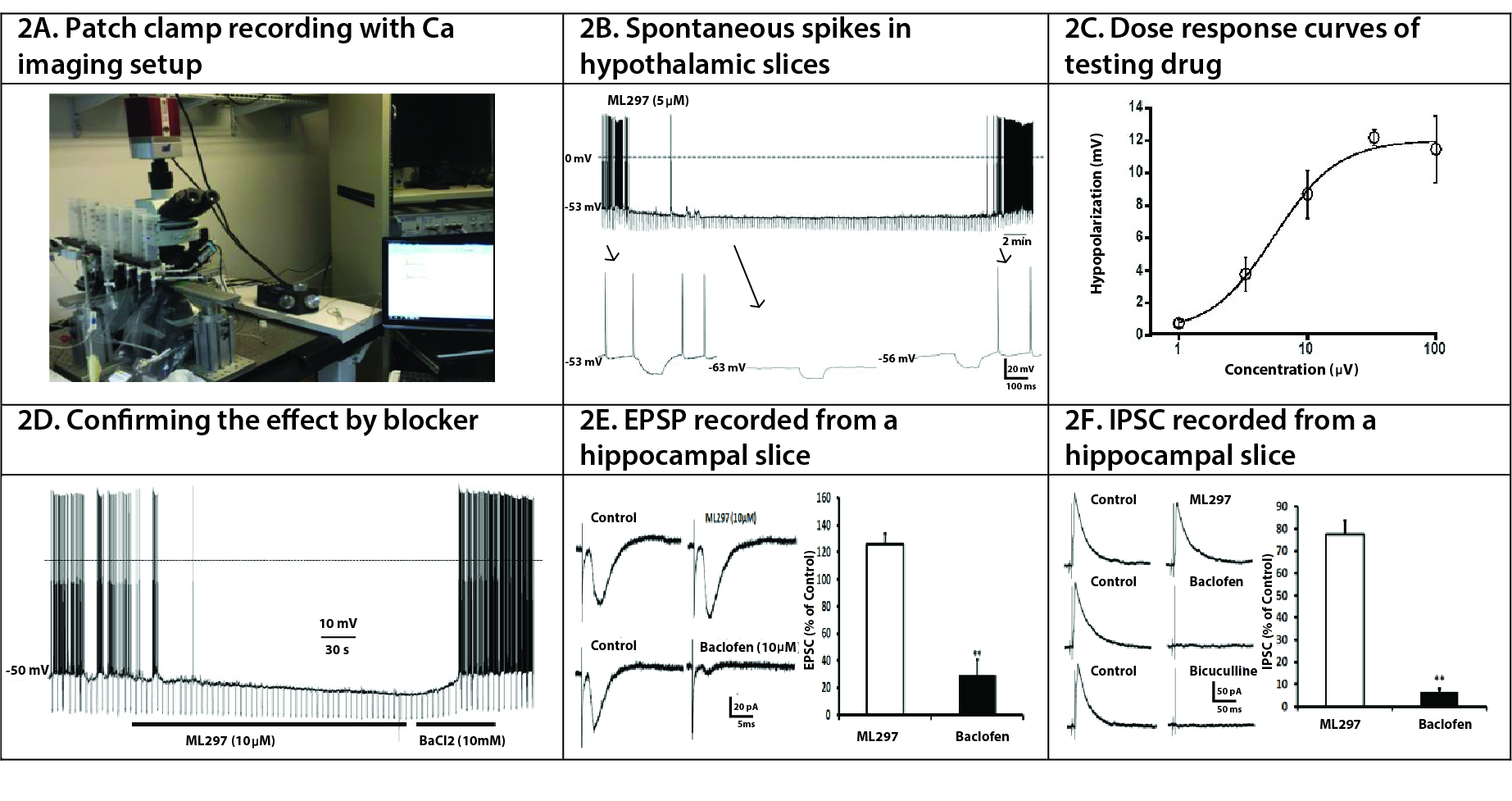
Figure 2. Mice were euthanized and the brains were quickly isolated and placed into ice-cold artificial cerebrospinal fluid (ACSF) continuously bubbled with 5% CO2/95% O2. The ACSF is composed of (in mM) NaCl 124.0, KCl 2.5, KH2PO4 1.2, CaCl2 2.4, MgSO4 1.3, NaHCO3 26.0 and glucose 10.0 (pH 7.4). Slices (260 μm thick) containing hippocampus and/or thalamus were prepared using a vibratome (Leica) and incubated at room temperature in continuously oxygenated ACSF for at least 1 h before recordings at room temperature. Slices were continuously perfused with ACSF bubbled with 5% CO2/95% O2 at a flow rate of 1 mL/min from an elevated reservoir. Recordings were made using an Axon 700B patch clamp amplifier, Axonpatch 1D for extracellular recordings, or a 64-channel multi-electrode array (MEA-64, Multi-Channel Systems).
Support Materials



