Newsletter
Proof-of-concept Studies: Cell and Gene Therapy CRO Services
Proof-of-concept or a determination of feasibility and rationale of a cell and gene therapy (CGT) product involves a complex mix of proof of efficacy of the product such a target specificity, ability to treat a pathophysiological condition as well as short-term and long-term safety in preclinical models. Such studies also include dose-ranging studies, biodistribution, transgene expression in case of gene therapy products, viral shedding in case of viral vector delivery, and immune response to the investigational CGT. When it comes to cell therapy, the requirements are even murkier. ASC’s multidisciplinary team of experts can help develop assays that would ease the path to an IND-submission.
Products and Services
Technical Details
Preclinical assessment of proof-of-concept (PoC) or proof-of-principle of investigational drugs is important step to decide the fate of drug candidates at an early developmental stage in order to reduce cost of drug attrition. The PoC studies in addition to preliminary efficacy studies in a clinically relevant cell line or animal model may also include proof of bioavailability, tolerability, and safety. Unlike traditional pharmaceutical-based drugs, for cell and gene therapy (CGT) candidates there is no specific battery of recommended tests. Each CGT has a unique mechanism of action or target, that necessitates development of assays specific to the drug being tested to assess its risk-benefit ratio.
ASC’s preclinical CRO platform leverages more than a decade’s expertise in genome editing technologies (including CRISPR/ Cas9), stem cell technologies, immuno-oncology, cell-based and gene therapy-based projects to help customers navigate the preclinical requirements for IND-submission for their CGTs. Starting from clinically relevant in vitro and in vivo model generation, we offer proof-of-concept assay development involving dose ranging, biodistribution, immunogenicity assessments, efficacy, transgene expression, viral genome distribution in rodents and NHP samples. We offer assays to detect drug efficacy at DNA/ RNA and protein levels through advanced qPCR, droplet-digital PCR (ddPCR), NGS, flow cytometry, RNAscope in situ hybridization assays, high content imaging of cells, cell-cell interaction, biomarker measurements and more.
Application Notes
Examples of Assay Development for a Recombinant Adeno-Associated Virus
Viral biodistribution in mouse tissue
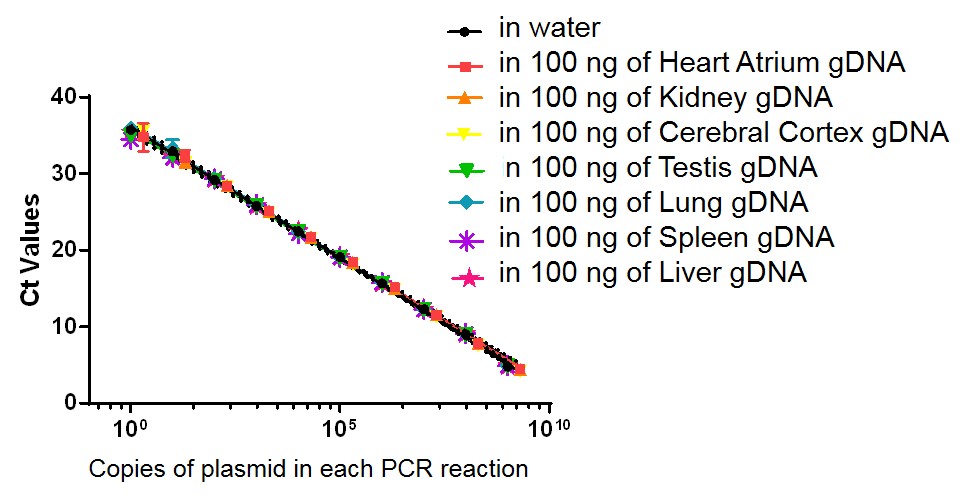
Figure. Standard curve developed to measure viral biodistribution for a recombinant adeno-associated viral (AAV) vector in mouse tissues. Genomic DNA (gDNA) sample from various tissues (heart, kidney, cerebral cortex, testis, lung, spleen, and liver) was extracted from PBS-only injected C57BL/6wild type (WT) mouse tissues, and added to a serial dilution of plasmid containing the gene of interest. Quantitative PCR (qPCR) was performed to generate a standard curve for the biodistribution of the gene of interest. Assay sensitivity: ≤50 copies of plasmid per 1 μg gDNA from mouse tissue. Note: No signal was detected in all negative controls (non-plasmid samples with and without tissue gDNA).
Virus shedding in human fluid samples
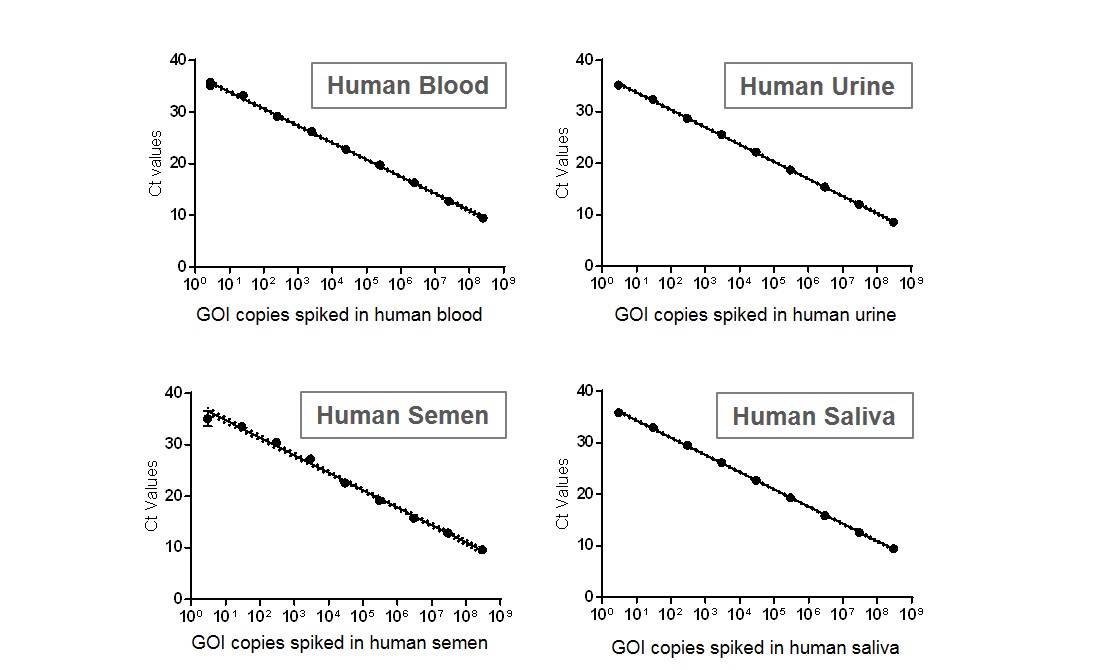
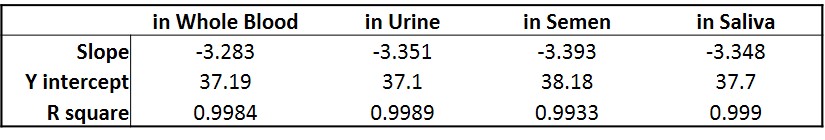
Figure. Standard curve developed to measure viral shedding of a recombinant adeno-associated viral (AAV) vector in human body fluid samples. A serial dilution of plasmid containing the gene of interest was spiked in various human body fluid samples (blood, urine, semen and saliva), and the DNA (both viral DNA and gDNA, if possible) was then extracted. Quantitative PCR (qPCR) was performed to generate a standard curve to measure viral shedding. Note: No signal was detected in all negative controls (DNA extracted from normal human body fluid samples without plasmid spiked-in).
Example of Pharmacodynamic (PD) Study to Evaluate CRISPR/Cas9 Genome Editing Efficiency of a Recombinant Adeno-Associated Viral Vector
In Vitro Indel detection using droplet digital PCR (ddPCR) following CRISPR-SaCas9 genome editing at a specific genetic locus of choice in HEK293T cells
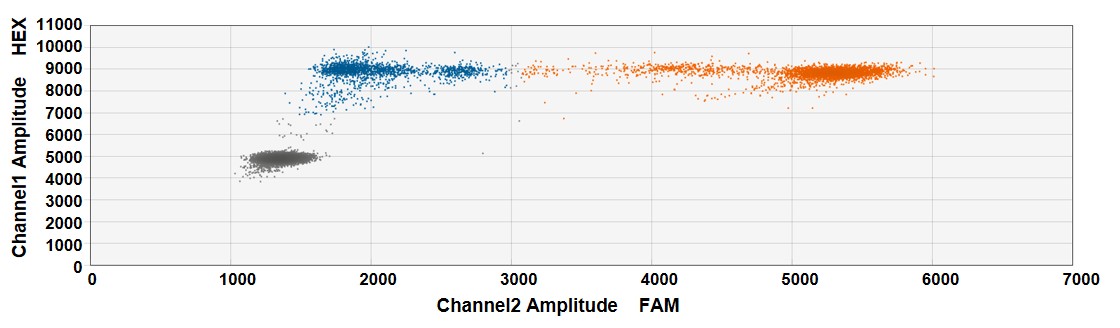
Figure. HEK293T cells in 12-well cell-culture plates were co-transfected with 0.5µg CMV-SaCas9 plasmid and 1µg U6-GuideRNA plasmid (1:2 ratio) using Lipofectamine3000. Indel detection at the locus was done by ddPCR using NHEJ genome editing detection drop-off assay (Bio-Rad) 48 hours post-transfection. The assay included one set of primers and two probes annealing the amplicon (FAM-labeled Reference probe and HEX-labeled Drop-off probe). Indel (blue, 37.6%) and unedited (orange) amplicon droplet populations are indicated. Gray droplets population includes droplet with no target sequence.


_L1.jpg)
